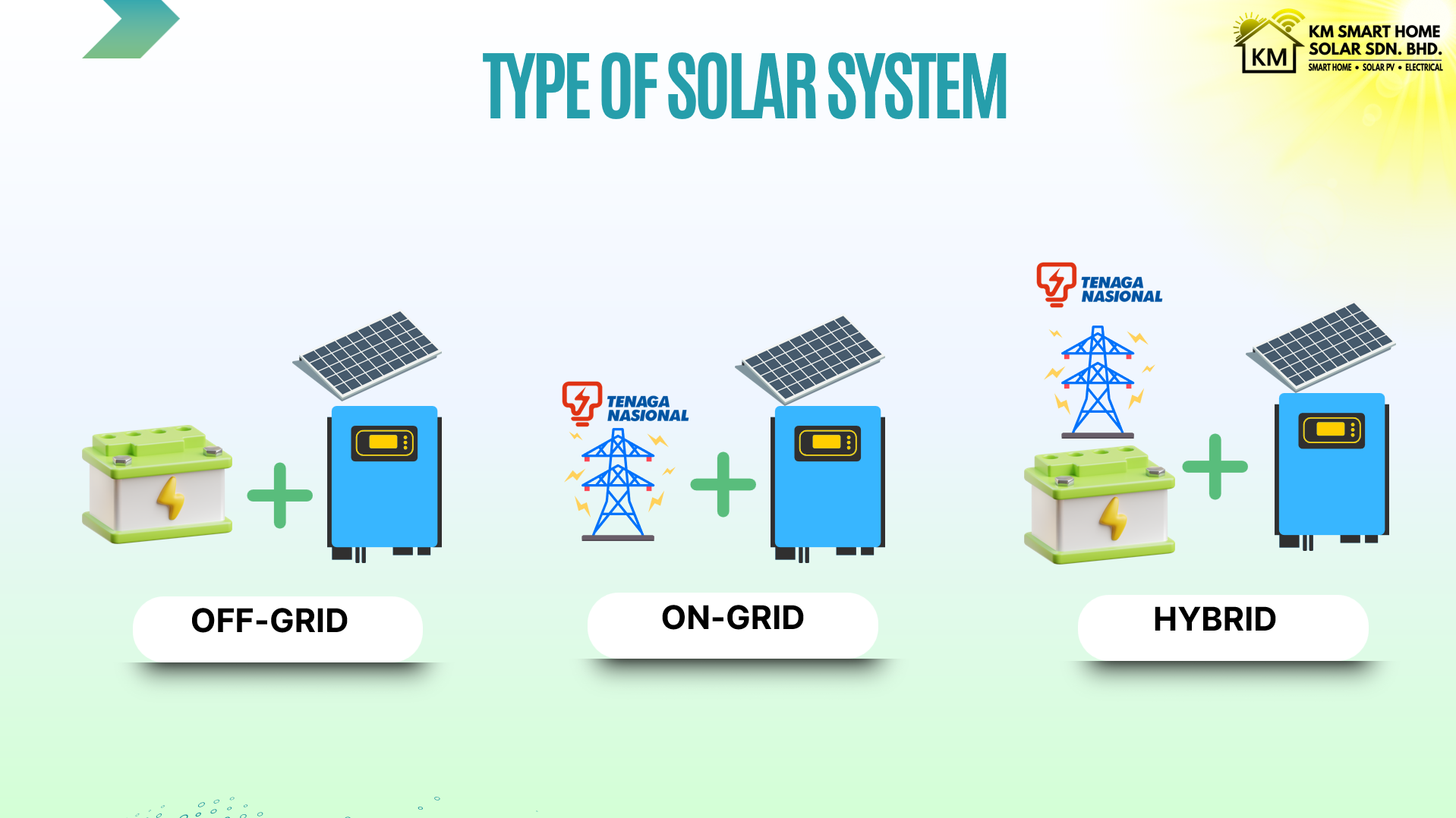
WHAT IS TYPE OF SOLAR PV SYSTEM ?
As the demand for renewable energy grows, understanding the types of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems becomes essential for making informed decisions about sustainable power solutions. There are three primary types of solar PV systems, each with unique advantages and best-use scenarios depending on factors such as grid access, energy needs, and environmental conditions. These types include grid-tied, off-grid, and hybrid systems.
1. Grid-Tied Solar PV System
A grid-tied solar PV system is directly connected to the local utility grid. Unlike systems that require batteries for energy storage, this type of setup draws power directly from the grid when solar production is low (for instance, at night or on cloudy days). Any excess energy generated by the system can be sent to the grid, potentially offsetting electricity costs.
Benefits: Grid-tied systems are cost-effective and provide reliable power without the need for batteries. Users benefit from a steady power supply by drawing from the grid during times of low solar generation.
Ideal Use: Grid-tied systems are best suited for homes and businesses located in areas with reliable access to a utility grid.
2. Off-Grid Solar PV System
Off-grid solar PV systems are entirely self-sufficient and independent of the utility grid. These systems rely on batteries to store energy generated during sunny periods, which can then be used during nights or cloudy weather. Off-grid systems provide complete energy independence, which can be crucial in remote or rural locations.
Benefits: With an off-grid system, users are entirely self-reliant, which is valuable for areas without stable or available grid access. This system enables sustainable living in remote regions.
Ideal Use: Off-grid systems are ideal for remote homes, cabins, or areas with limited or unreliable grid connectivity.
3. Hybrid Solar PV System
A hybrid solar PV system combines features of both grid-tied and off-grid systems. It remains connected to the utility grid while also incorporating batteries for energy storage. This flexibility allows users to store excess energy for use during peak hours, power outages, or periods of low sunlight.
Benefits: Hybrid systems offer grid backup with additional energy independence. They allow users to save on energy costs during peak hours and provide reliable power during outages.
Ideal Use: Hybrid systems work well in areas prone to power outages or with variable energy prices, where having backup storage helps manage costs effectively.
Choosing the Right Solar PV System
The choice of solar PV system should be based on the specific needs of the location, energy usage patterns, and access to a reliable grid. Grid-tied systems are generally the most economical for urban settings with steady grid access, while off-grid systems are vital for remote locations. Hybrid systems are particularly useful in areas where outages are frequent, or where energy costs fluctuate throughout the day.
Each of these solar PV systems offers a viable way to harness renewable energy, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient energy future.